The Microsoft .Net Framework is a platform that
provides tools and technologies you need to build Networked Applications
as well as Distributed Web Services and Web Applications. The .Net
Framework provides the necessary compile time and run-time foundation to
build and run any language that conforms to the Common Language Specification (CLS).The main two components of .Net Framework are Common Language Runtime (CLR) and .Net Framework Class Library (FCL).
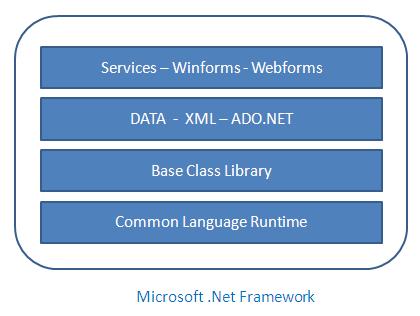
The Common Language Runtime
(CLR) is the runtime environment of the .Net Framework , that executes
and manages all running code like a Virtual Machine. The .Net Framework Class Library
(FCL) is a huge collection of language-independent and type-safe
reusable classes. The .Net Framework Class Libraries (FCL) are arranged
into a logical grouping according to their functionality and usability
is called Namespaces. In the following sections describes how to .Net Framework manages the code in compile time and run time .
Microsoft .NET (pronounced “dot net”) is a software component that
runs on the Windows operating system. .NET provides tools and libraries
that enable developers to create Windows software much faster and
easier. .NET benefits end-users by providing applications of higher
capability, quality and security. The .NET Framework must be installed
on a user’s PC to run .NET applications.
This is how Microsoft describes it: “.NET is the Microsoft Web
services strategy to connect information, people, systems, and devices
through software. Integrated across the Microsoft platform, .NET
technology provides the ability to quickly build, deploy, manage, and
use connected, security-enhanced solutions with Web services.
.NET-connected solutions enable businesses to integrate their systems
more rapidly and in a more agile manner and help them realize the
promise of information anytime, anywhere, on any device.” See Microsoft for more information.
.NET is both a business strategy from Microsoft and its collection of programming support for what are known as Web services,
the ability to use the Web rather than your own computer for various
services. Microsoft's goal is to provide individual and business users
with a seamlessly interoperable and Web-enabled interface for
applications and computing devices and to make computing activities
increasingly Web browser-oriented.
The .NET platform includes servers; building-block services, such as
Web-based data storage; and device software. It also includes Passport,
Microsoft's fill-in-the-form-only-once identity verification service.
- The ability to make the entire range of computing devices work together and to have user information automatically updated and synchronized on all of them
- Increased interactive capability for Web sites, enabled by greater use of XML (Extensible Markup Language) rather than HTML
- A premium online subscription service, that will feature customized access and delivery of products and services to the user from a central starting point for the management of various applications, such as e-mail, for example, or software, such as Office .NET
- Centralized data storage, which will increase efficiency and ease of access to information, as well as synchronization of information among users and devices
- The ability to integrate various communications media, such as e-mail, faxes, and telephones
- For developers, the ability to create reusable modules, which should increase productivity and reduce the number of programming errors
The full release of .NET is expected to take several years to complete, with intermittent releases of products such as a personal security service and new versions of Windows and Office that implement the .NET strategy coming on the market separately. Visual Studio .NET is a development environment that is now available. Windows XP supports certain .NET capabilities.
 03:57
03:57
 VISHAL PANDYA
VISHAL PANDYA


 Posted in:
Posted in: 

0 comments:
Post a Comment